思考并回答以下问题:
前言
数据库表通常相互关联。Laravel中的模型关联功能使得关于数据库的关联代码变得更加简单,更加优雅。本文会详细说说关于模型关联的源码,以便更好的理解和使用关联模型。
定义关联
所谓的定义关联,就是在一个Model中定义一个关联函数,我们利用这个关联函数去操作另外一个Model,例如,user表是用户表,posts是用户发的文章,一个用户可以发表多篇文章,我们就可以这样写:1
$user->posts()->where('active', 1)->get();
这表明了我们想通过$user这个用户查询到状态active为1的所有文章,posts就是关联函数,我们可以通过这个关联函数去操作另一个与user关联的表。
在说模型关联的定义之前,我们要先说说父模型与子模型的概念。所谓的父模型是指在模型关系中主动的一方,例如用户模型和文章模型中的用户,相应的子模型就是模型关系中的被动一方,例如文章模型。在正向定义中,被关联的是子模型,而在反向关联中,被关联的是父模型。
我们知道,关联有多种形式,各种关系如下:
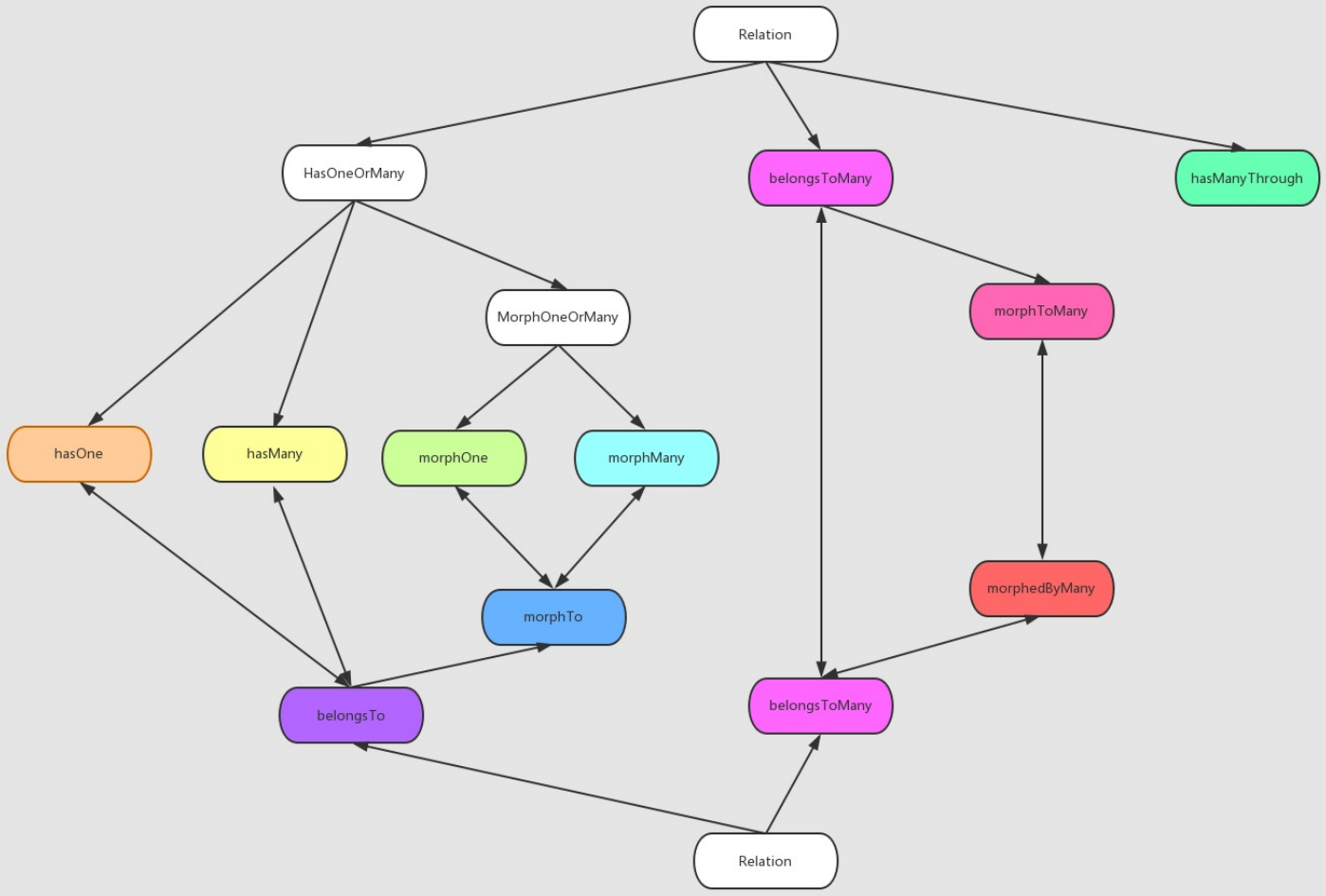
hasOne一对一
我们以官方文档的例子来说明,一个User模型可能关联一个Phone模型:
1 | class User extends Model |
我们来看看hasOne的源码:
1 | namespace Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Concerns; |
newRelatedInstance函数负责建立一个新的被关联的模型实例,主要目的是设置数据库连接:
1 | /** |
在一对一的关系中,foreignKey外键名默认是父模型的类名和主键名的蛇形变量,localKey是父模型的主键名:
1 | namespace Illuminate\Database\Eloquent; |
hasOne函数的构造函数继承HasOneOrMany类,也就是说,一对一与一对多构造函数相同,这部分主要设置外键名:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21namespace Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Relations;
abstract class HasOneOrMany extends Relation
{
/**
* Create a new has one or many relationship instance.
*
* @param \Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Builder $query
* @param \Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model $parent
* @param string $foreignKey
* @param string $localKey
* @return void
*/
public function __construct(Builder $query, Model $parent, $foreignKey, $localKey)
{
$this->localKey = $localKey;
$this->foreignKey = $foreignKey;
parent::__construct($query, $parent);
}
}
HasOneOrMany类继承Relation类,这部分主要设置parent(父模型)、被关联模型(子模型)与被关联模型(子模型)的查询构造器:
1 | namespace Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Relations; |
hasOne的模型关系如下:
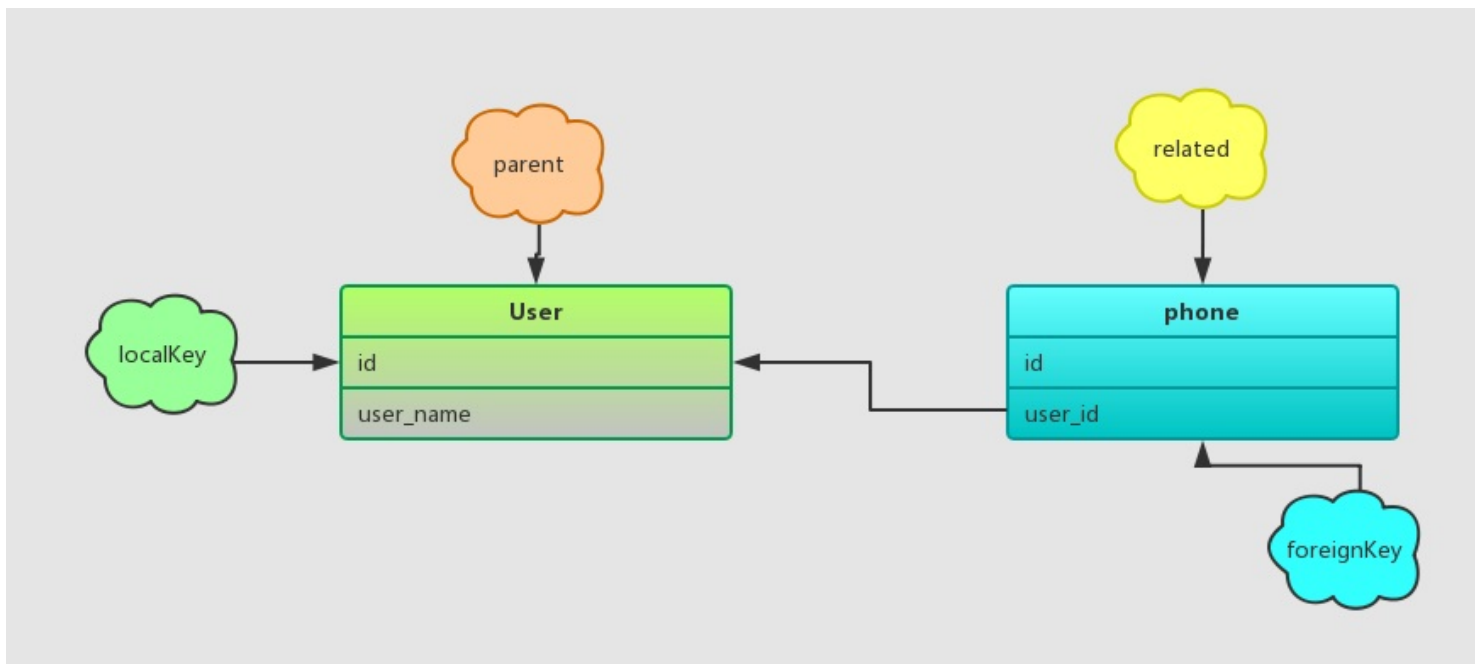
除了保存被关联模型的查询构造器、被关联模型与parent模型之外,还会提供额外的限制条件:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24/**
* Set the base constraints on the relation query.
*
* @return void
*/
public function addConstraints()
{
if (static::$constraints)
{
$this->query->where($this->foreignKey, '=', $this->getParentKey());
$this->query->whereNotNull($this->foreignKey);
}
}
/**
* Get the key value of the parent's local key.
*
* @return mixed
*/
public function getParentKey()
{
return $this->parent->getAttribute($this->localKey);
}
限制条件为被关联模型和关联模型建立外键约束关系:1
select phone where phone.user_id = 1 (user.id)
hasMany一对多
在模型关联的定义中,一对一与一对多源码是一样的:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25namespace Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Concerns;
trait HasRelationships
{
/**
* Define a one-to-many relationship.
*
* @param string $related
* @param string|null $foreignKey
* @param string|null $localKey
* @return \Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Relations\HasMany
*/
public function hasMany($related, $foreignKey = null, $localKey = null)
{
$instance = $this->newRelatedInstance($related);
$foreignKey = $foreignKey ?: $this->getForeignKey();
$localKey = $localKey ?: $this->getKeyName();
return $this->newHasMany(
$instance->newQuery(), $this, $instance->getTable().'.'.$foreignKey, $localKey
);
}
}
hasMany的模型关系如下:
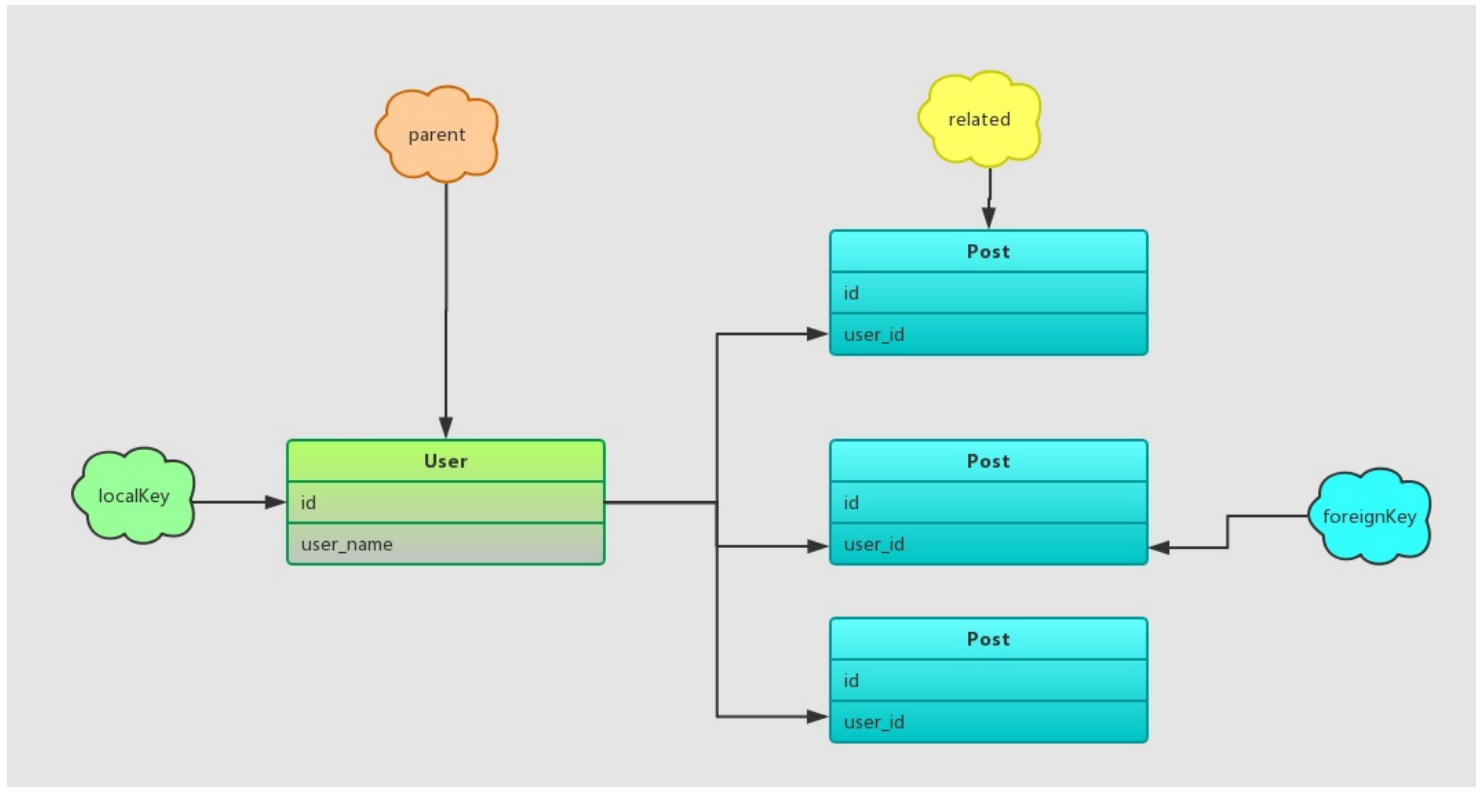
限制条件与一对一相同,为被关联模型和关联模型建立外键约束关系:1
select phone where phone.user_id = 1 (user.id)
belongsTo一对一、一对多反向关联
如果想要从文章反向查找作者用户,那么可以定义反向关联:
1 | public function user() |
belongsTo源码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43namespace Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Concerns;
trait HasRelationships
{
/**
* Define an inverse one-to-one or many relationship.
*
* @param string $related
* @param string|null $foreignKey
* @param string|null $ownerKey
* @param string|null $relation
* @return \Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Relations\BelongsTo
*/
public function belongsTo($related, $foreignKey = null, $ownerKey = null, $relation = null)
{
// If no relation name was given, we will use this debug backtrace to extract
// the calling method's name and use that as the relationship name as most
// of the time this will be what we desire to use for the relationships.
if (is_null($relation))
{
$relation = $this->guessBelongsToRelation();
}
$instance = $this->newRelatedInstance($related);
// If no foreign key was supplied, we can use a backtrace to guess the proper
// foreign key name by using the name of the relationship function, which
// when combined with an "_id" should conventionally match the columns.
if (is_null($foreignKey))
{
$foreignKey = Str::snake($relation).'_'.$instance->getKeyName();
}
// Once we have the foreign key names, we'll just create a new Eloquent query
// for the related models and returns the relationship instance which will
// actually be responsible for retrieving and hydrating every relations.
$ownerKey = $ownerKey ?: $instance->getKeyName();
return $this->newBelongsTo(
$instance->newQuery(), $this, $foreignKey, $ownerKey, $relation
);
}
}
正向定义与反向定义不同的是多了一个参数relation,这个参数默认值是从debug_backtrace函数获取的:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11/**
* Guess the "belongs to" relationship name.
*
* @return string
*/
protected function guessBelongsToRelation()
{
[$one, $two, $caller] = debug_backtrace(DEBUG_BACKTRACE_IGNORE_ARGS, 3);
return $caller['function'];
}
也就是我们的关联函数名user,belongsTo函数会将关联函数名作为关联名保存起来。
另一个不同是外键的默认名称,不再是类名+主键名,而是关联名+主键名:1
2
3
4if (is_null($foreignKey))
{
$foreignKey = Str::snake($relation).'_'.$instance->getKeyName();
}
我们接着看belongsTo函数:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18namespace Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Relations;
class BelongsTo extends Relation
{
public function __construct(Builder $query, Model $child, $foreignKey, $ownerKey, $relationName)
{
$this->ownerKey = $ownerKey;
$this->relationName = $relationName;
$this->foreignKey = $foreignKey;
// In the underlying base relationship class, this variable is referred to as
// the "parent" since most relationships are not inversed. But, since this
// one is we will create a "child" variable for much better readability.
$this->child = $child;
parent::__construct($query, $child);
}
}
我们可以看出来,相对于正向关联,反向关联除了保存外键名与主键名之外,还保存了关系名、子模型。值得注意的是,反向关联中related代表父模型,parent代表子模型,与正向关联相反。
hasMany的模型关系如下:
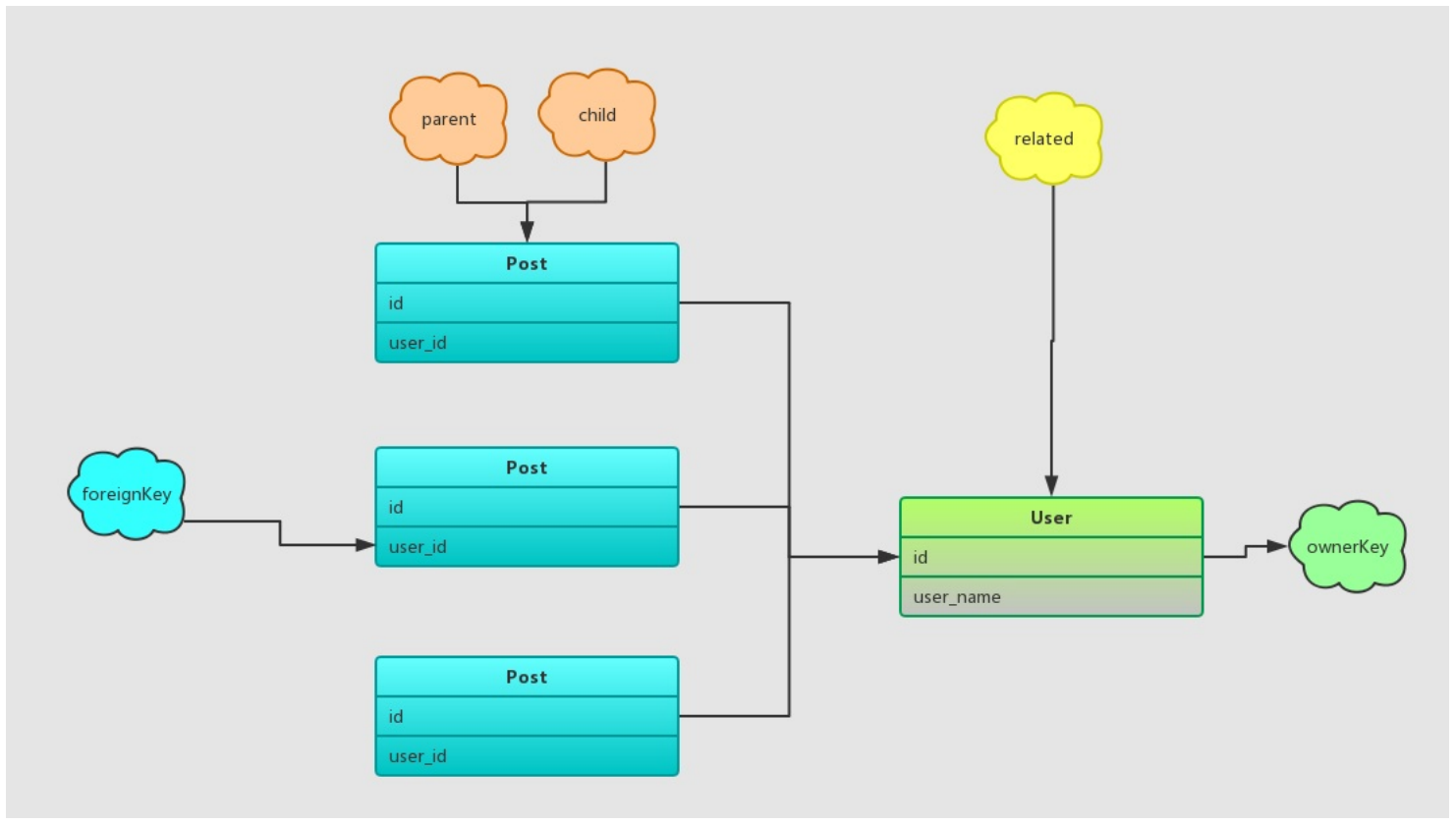
约束条件也相应地进行反转改变:
1 | public function addConstraints() |
限制条件:1
select user where user.id = 1 (post.user_id)
belongsMany多对多
多对多关系由于中间表的原因相对来说比较复杂,涉及的参数也非常多。我们以官网例子:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10class User extends Model
{
/**
* 获得此用户的角色。
*/
public function roles()
{
return $this->belongsToMany('App\Role', 'role_user', 'user_id', 'role_id');
}
}
User表与role表是多对多关系,另外有一中间表user_role表,我们在定义关系的时候,related是被关联模型,table是中间表,foreignPivotKey是中间表中父模型外键名,relatedPivotKey是中间表中子模型外键名,parentKey是父模型主键名,relatedKey是子模型主键名,relation是关系名。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21public function belongsToMany($related, $table = null, $foreignP
ivotKey = null, $relatedPivotKey = null, $parentKey = null, $rel
atedKey = null, $relation = null)
{
if (is_null($relation)) {
$relation = $this->guessBelongsToManyRelation();
}
$instance = $this->newRelatedInstance($related);
$foreignPivotKey = $foreignPivotKey ?: $this->getForeignKey(
);
$relatedPivotKey = $relatedPivotKey ?: $instance->getForeign
Key();
if (is_null($table)) {
$table = $this->joiningTable($related);
}
return new BelongsToMany(
$instance->newQuery(), $this, $table, $foreignPivotKey,
$relatedPivotKey, $parentKey ?: $this->getKeyName(),
$relatedKey ?: $instance->getKeyName(), $relation
);
}
获取关联名称仍然使用的是debug_backtrace函数,不同于guessBelongsToRelation函数只有 belongsTo调用,guessBelongsToManyRelation函数还可以被morphedByMany函数调用,所以不能单纯的限制返回堆栈帧:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14public static $manyMethods = [
'belongsToMany', 'morphToMany', 'morphedByMany',
'guessBelongsToManyRelation', 'findFirstMethodThatIsntRelati
on',
];
protected function guessBelongsToManyRelation()
{
$caller = Arr::first(debug_backtrace(DEBUG_BACKTRACE_IGNORE_
ARGS), function ($trace) {
return ! in_array($trace['function'], Model::$manyMethod
s);
});
return ! is_null($caller) ? $caller['function'] : null;
}
默认的中间表是两个表名的蛇形变量:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9public function joiningTable($related)
{
$models = [
Str::snake(class_basename($related)),
Str::snake(class_basename($this)),
];
sort($models);
return strtolower(implode('_', $models));
}
BelongsToMany的初始化也需要保存这些变量:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13public function __construct(Builder $query, Model $parent, $tabl
e, $foreignPivotKey,
$relatedPivotKey, $parentKey, $r
elatedKey, $relationName = null)
{
$this->table = $table;
$this->parentKey = $parentKey;
$this->relatedKey = $relatedKey;
$this->relationName = $relationName;
$this->relatedPivotKey = $relatedPivotKey;
$this->foreignPivotKey = $foreignPivotKey;
parent::__construct($query, $parent);
}
belongsToMany 的模型关系如下:
反向的多对多模型关系:
限制条件:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24public function addConstraints()
{
$this->performJoin();
if (static::$constraints) {
$this->addWhereConstraints();
}
}
protected function performJoin($query = null)
{
$query = $query ?: $this->query;
$baseTable = $this->related->getTable();
$key = $baseTable.'.'.$this->relatedKey;
$query->join($this->table, $key, '=', $this->getQualifiedRel
atedPivotKeyName());
return $this;
}
protected function addWhereConstraints()
{
$this->query->where(
$this->getQualifiedForeignPivotKeyName(), '=', $this->pa
rent->{$this->parentKey}
);
return $this;
}
本例中wher条件:1
2select role join role_user on role_user.role_id = 1 (role.id)
select role where role_user.user_id = 1 (user.id)
hasManyThrough远程一对多
远程一对多关联提供了方便、简短的方式通过中间的关联来获得远层的关联。以官方例子来看:
1 | class Country extends Model |
可以看到,远程一对多的参数比较多。第一个参数related是最终被关联的模型,through是中间模型,firstKey是中间模型关于父模型的外键,secondKey是最终被关联的模型关于中间模型的外键,localKey是父模型的主键,secondLocalKey是中间模型的主键:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12public function hasManyThrough($related, $through, $firstKey = n
ull, $secondKey = null, $localKey = null, $secondLocalKey = null)
{
$through = new $through;
$firstKey = $firstKey ?: $this->getForeignKey();
$secondKey = $secondKey ?: $through->getForeignKey();
$localKey = $localKey ?: $this->getKeyName();
$secondLocalKey = $secondLocalKey ?: $through->getKeyName();
$instance = $this->newRelatedInstance($related);
return new HasManyThrough($instance->newQuery(), $this, $thr
ough, $firstKey, $secondKey, $localKey, $secondLocalKey);
}
HasManyThrough的初始化:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12public function __construct(Builder $query, Model $farParent, Mo
del $throughParent, $firstKey, $secondKey, $localKey, $secondLoc
alKey)
{
$this->localKey = $localKey;
$this->firstKey = $firstKey;
$this->secondKey = $secondKey;
$this->farParent = $farParent;
$this->throughParent = $throughParent;
$this->secondLocalKey = $secondLocalKey;
parent::__construct($query, $throughParent);
}
hasManyThrough的模型关系如下:
限制条件:
1 | public function addConstraints() |
本例中的限制条件:
1 | select post join user on user.id = post.user_id |
morphOne/morphMany多态关联
多态关联允许我们应用一个表来单独作为多个表的属性,多态关联存在一对一、一对多、多对多的情形。所谓一对一、一对多是指,一个模型只拥有一个属性或多个属性,例如官网中的例子:
用户可以「评论」文章和视频。使用多态关联,您可以用一个comments表同时满足这两个使用场景
1 | class Post extends Model |
这个 comments 表就是属性表,当文章和视频只能有一个评论的时候,那么就是一对一多态关联;如果文章和视频可以由多个评论的时候,就是一对多多态关联。
这种属性表一般会有两个固定的字段: commentable_type用于标识该条评论是文章的还是视频的、 commentable_id 用于记录文章或视频的主键 id 。
我们可以把多态关联看作普通的一对一、一对多关系,只是外键参数是 type 与id 的组合。
related 是属性表,也就是这里的 comments ,type参数是属性表中存储父模型类型的列名(commentable_type), id 参数是属性表中存储父模型主键的列名(commentable_id),而name专用于省略type参数与id参数,localKey是指父模型的主键。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24public function morphOne($related, $name, $type = null, $id = nu
ll, $localKey = null)
{
$instance = $this->newRelatedInstance($related);
list($type, $id) = $this->getMorphs($name, $type, $id);
$table = $instance->getTable();
$localKey = $localKey ?: $this->getKeyName();
return new MorphOne($instance->newQuery(), $this, $table.'.'
.$type, $table.'.'.$id, $localKey);
}
public function morphMany($related, $name, $type = null, $id = n
ull, $localKey = null)
{
$instance = $this->newRelatedInstance($related);
list($type, $id) = $this->getMorphs($name, $type, $id);
$table = $instance->getTable();
$localKey = $localKey ?: $this->getKeyName();
return new MorphMany($instance->newQuery(), $this, $table.'.'
.$type, $table.'.'.$id, $localKey);
}
protected function getMorphs($name, $type, $id)
{
return [$type ?: $name.'_type', $id ?: $name.'_id'];
}
一对一、一对多多态关联主要保存属性表中表示类型的列名,还有需要向该类型列中写入的父模型名称,一般来说,默认会写父模型的类名( App\Post 、 App\Video )1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16public function __construct(Builder $query, Model $parent, $type
, $id, $localKey)
{
$this->morphType = $type;
$this->morphClass = $parent->getMorphClass();
parent::__construct($query, $parent, $id, $localKey);
}
public function getMorphClass()
{
$morphMap = Relation::morphMap();
if (! empty($morphMap) && in_array(static::class, $morphMap)
) {
return array_search(static::class, $morphMap, true);
}
return static::class;
}
不过我们也可以自定义写入的值:
1 | Relation::morphMap([ |
这样,就会把App\Post换成posts, App\Video换成videos。我们来看看这个多态映射表函数:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20public static function morphMap(array $map = null, $merge = true)
{
$map = static::buildMorphMapFromModels($map);
if (is_array($map)) {
static::$morphMap = $merge && static::$morphMap
? array_merge(static::$morphMap, $map) :
$map;
}
return static::$morphMap;
}
protected static function buildMorphMapFromModels(array $models
= null)
{
if (is_null($models) || Arr::isAssoc($models)) {
return $models;
}
return array_combine(array_map(function ($model) {
return (new $model)->getTable();
}, $models), $models);
}
可以看到, buildMorphMapFromModels 函数将字符串App\Post转为model,并利用array_combine转为键。
morphOne的模型关系如下:
morphMany的模型关系如下:
限制条件:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16public function addConstraints()
{
if (static::$constraints) {
parent::addConstraints();
$this->query->where($this->morphType, $this->morphClass)
;
}
}
public function addConstraints()
{
if (static::$constraints) {
$this->query->where($this->foreignKey, '=', $this->getPa
rentKey());
$this->query->whereNotNull($this->foreignKey);
}
}
本例中的限制条件:1
2
3select comments where comment.commentable_id = post.id
select comments where comment.commentable_id is not null
select comments where comment.commentable_type = 'App\Post'
morphTo 反向多态关联
和一对一、一对多的 belongsTo 相似,多态关联还可以定义反向关联morphTo :1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10class Comment extends Model
{
/**
* 获得拥有此评论的模型。
*/
public function commentable()
{
return $this->morphTo();
}
}
与 belongsTo 类似, morphTo 也是利用 debug_backtrace 获取关联名称。
当前如果正处于预加载状态的时候, Comment 一般还没有从数据库获取数据,$this->{$type}是空值,这个时候需要去除预加载来初始化:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28public function morphTo($name = null, $type = null, $id = null)
{
$name = $name ?: $this->guessBelongsToRelation();
list($type, $id) = $this->getMorphs(
Str::snake($name), $type, $id
);
return empty($class = $this->{$type})
? $this->morphEagerTo($name, $type, $id)
: $this->morphInstanceTo($class, $name, $type, $
id);
}
protected function morphEagerTo($name, $type, $id)
{
return new MorphTo(
$this->newQuery()->setEagerLoads([]), $this, $id, null,
$type, $name
);
}
protected function morphInstanceTo($target, $name, $type, $id)
{
$instance = $this->newRelatedInstance(
static::getActualClassNameForMorph($target)
);
return new MorphTo(
$instance->newQuery(), $this, $id, $instance->getKeyName
(), $type, $name
);
}
多态的成员变量 morphType 代表属性表的类型列, morphClass MorphTo的成员变量只有一个 morphType :1
2
3
4
5
6
7public function __construct(Builder $query, Model $parent, $fore
ignKey, $ownerKey, $type, $relation)
{
$this->morphType = $type;
parent::__construct($query, $parent, $foreignKey, $ownerKey,
$relation);
}
morphTo 的模型关系如下:
限制条件与 belongsTo 相同:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8public function addConstraints()
{
if (static::$constraints) {
$table = $this->related->getTable();
$this->query->where($table.'.'.$this->ownerKey, '=', $th
is->child->{$this->foreignKey});
}
}
本例中的限制条件
1 | select post where post.id = comments.commentable_id |
多对多多态关联
除了传统的多态关联,您也可以定义「多对多」的多态关联。例如,Post模型和Video模型可以共享一个多态关联至 Tag 模型。 使用多对多多态关联可以让您在文章和视频中共享唯一的标签列表。
1 | class Post extends Model |
多对多多态关联与多对多关联的代码类似,不同的是中间表不再是两个父模型的蛇形变量,而是name的复数,值得注意的是foreignPivotKey代表中间表中对当前post或者video的外键,一般会放在taggable_id字段中,relatedPivotKey代表中间表中对属性表 tag 的外键 tag_id :1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21public function morphToMany($related, $name, $table = null, $for
eignPivotKey = null,
$relatedPivotKey = null, $parent
Key = null,
$relatedKey = null, $inverse = f
alse)
{
$caller = $this->guessBelongsToManyRelation();
$instance = $this->newRelatedInstance($related);
$foreignPivotKey = $foreignPivotKey ?: $name.'_id';
$relatedPivotKey = $relatedPivotKey ?: $instance->getForeign
Key();
$table = $table ?: Str::plural($name);
return new MorphToMany(
$instance->newQuery(), $this, $name, $table,
$foreignPivotKey, $relatedPivotKey, $parentKey ?: $this-
>getKeyName(),
$relatedKey ?: $instance->getKeyName(), $caller, $invers
e
);
}
MorphToMany的构造函数依然有morphType与morphClass,morphType标识着当前中间表的记录类型是Post,还是videos,morphClass的值默认值是Post类或者videos的全名,正向关联的时候, inverse是false,反向关联的时候,inverse是true 。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14public function __construct(Builder $query, Model $parent, $nam
e, $table, $foreignPivotKey,
$relatedPivotKey, $parentKey, $r
elatedKey, $relationName = null, $inverse = false)
{
$this->inverse = $inverse;
$this->morphType = $name.'_type';
$this->morphClass = $inverse ? $query->getModel()->getMorphC
lass() : $parent->getMorphClass();
parent::__construct(
$query, $parent, $table, $foreignPivotKey,
$relatedPivotKey, $parentKey, $relatedKey, $relationName
);
}
正向关联的时候, parent 类是 Post 类或者 videos 类,反向关联的时候related 是 Post 类或者 videos 类。
限制条件:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19protected function addWhereConstraints()
{
parent::addWhereConstraints();
$this->query->where($this->table.'.'.$this->morphType, $this
->morphClass);
return $this;
}
protected function addWhereConstraints()
{
$this->query->where(
$this->getQualifiedForeignPivotKeyName(), '=', $this->pa
rent->{$this->parentKey}
);
return $this;
}
public function getQualifiedForeignPivotKeyName()
{
return $this->table.'.'.$this->foreignPivotKey;
}
官网中例子限制条件转化为 sql (假设 Post 的主键为 1) :
1 | where taggables.taggable_id = 1; |
morphToMany 的模型关系如下:
限制条件:
1 | public function addConstraints() |
本例中的限制条件:1
2
3select tag join tagable on tagable.tag_id = tag.id
select tags where tagable.tagables_id = post.id
select tags where tagable.tagables_type = 'App\Tag'
多对多多态反向关联
官方文档例子:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10class Tag extends Model
{
/**
* 获得此标签下所有的文章。
*/
public function posts()
{
return $this->morphedByMany('App\Post', 'taggable');
}
}
与正向关联相反,relatedPivotKey代表中间表中对related表post或者video的外键,一般会放在taggable_id字段中, foreignPivotKey代表中间表中对当前属性表tag的外键tag_id:
1 | public function morphedByMany($related, $name, $table = null, $f |
官网中例子限制条件转化为 sql (假设 Tag 的主键为 1) :
1 | where taggables.tag_id = 1; |
morphedByMany 的模型关系如下:
限制条件与 morphToMany 一致:
1 | public function addConstraints() |
本例中的限制条件1
2
3select post join post on post.id = tagables.tagable_id
select post where tagables.tag_id = tag.id
select post where tagables.tagable_type = 'App\Post'